Reactive Oxygen Species
From Formation to Cellular Impact
Reactive Oxygen Species
From Formation to Cellular Impact
Reactive Oxygen Species
Reactive Oxygen Species
Key Driver of Cellular Damage and Disease
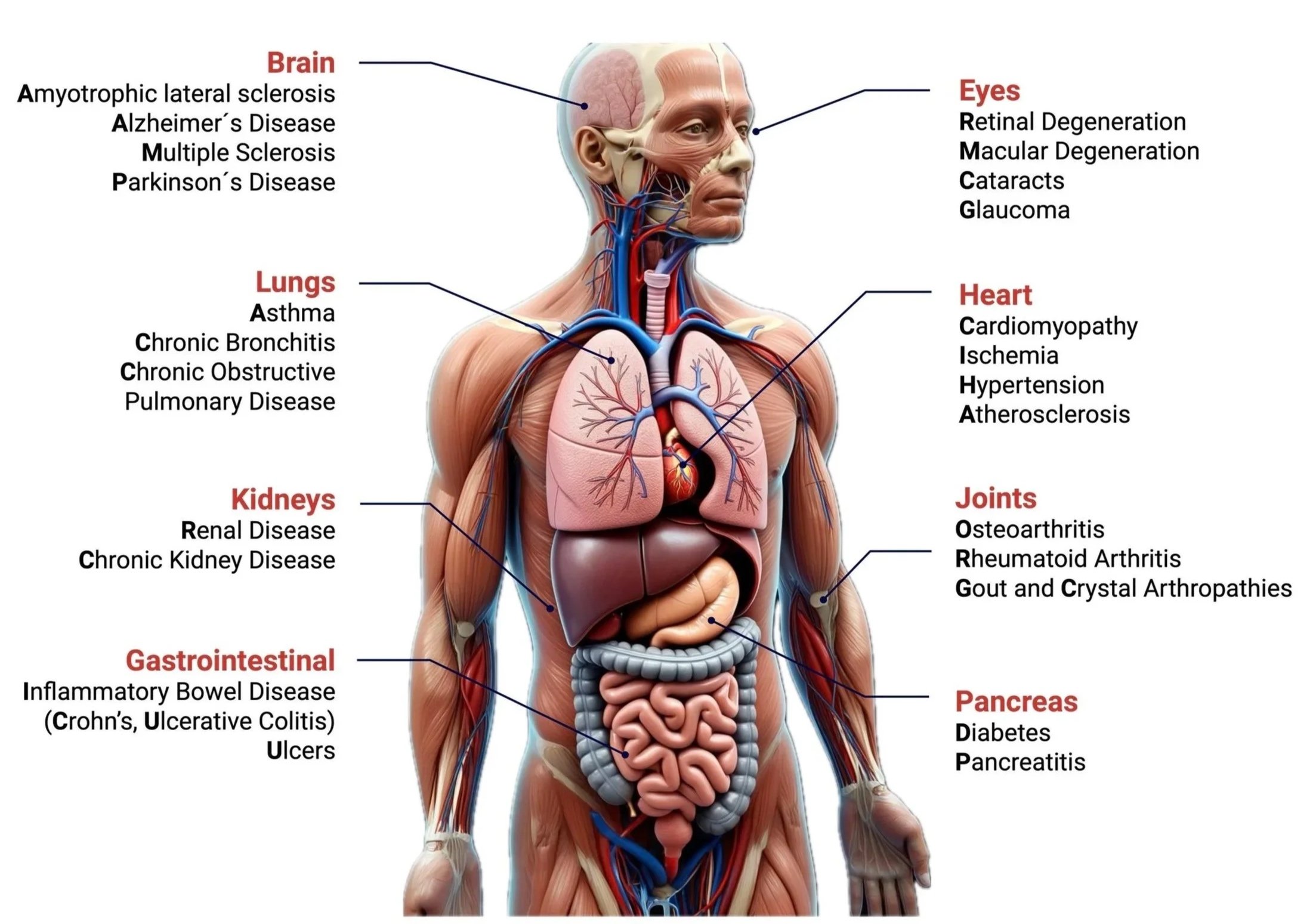
Oxygen is vital for Life, but its use in Cells inevitably generates Reactive Oxygen (ROS) and Nitrogen (RNS) Species - unstable Molecules that readily react with surrounding Structures. When their Levels overwhelm the Body’s Antioxidant Defenses, a Condition called Oxidative Stress, they damage DNA, proteins, and lipids, undermining Cell Health and driving Disease.
Oxygen is vital for Life, but its use in Cells inevitably generates Reactive Oxygen (ROS) and Nitrogen (RNS) Species - unstable Molecules that readily react with surrounding Structures. When their Levels overwhelm the Body’s Antioxidant Defenses, a Condition called Oxidative Stress, they damage DNA, proteins, and lipids, undermining Cell Health and driving Disease.
Sources of Free Radicals
Free Radicals arise both inside the Body and from the Environment.
Internal (endogenous): They are Byproducts of normal Processes such as Energy Production in Mitochondria, Enzyme Activity during Metabolism and Inflammation, and Immune Cells releasing Radicals to fight Infections.
External (exogenous): They are also triggered by outside Factors like Radiation, Pollution, Smoking, Alcohol, Processed Foods, and certain Drugs, all of which can raise Oxidative Stress.
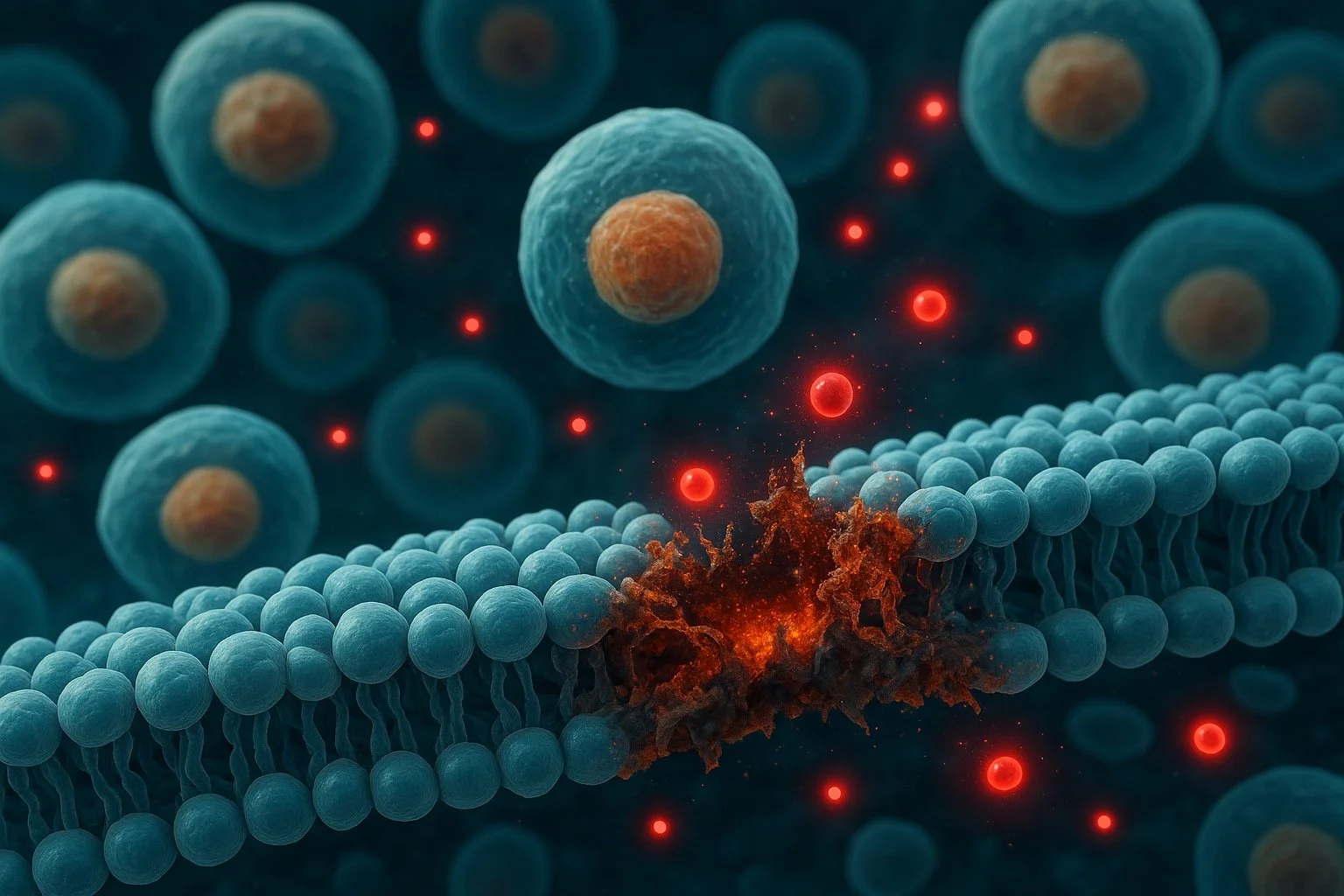
When produced in excess, ROS and RNS attack vital cellular components, disrupting function and driving disease.
How Free Radicals Damage the Body
DNA Damage
ROS/RNS break Nuclear and Mitochondrial DNA Strands, modify Bases, and impair Repair, leading to Mutations, Genomic Instability, Cancer, Aging, and Immune Activation.
Protein Oxidation
ROS/RNS alter Protein Structure and Function, causing Side-Chain oxidation, misfolding, Enzyme inactivation, Mitochondrial dysfunction, and ultimately Cell Death or Immune Responses.
Lipid Peroxidation
ROS/RNS damage Membrane Lipids, generating toxic Byproducts, destabilizing Membranes, disrupting Signaling, oxidizing LDL, and promoting Inflammation and Tissue Injury.
Oxidative Damage
The Common Root Cause Linking Major Diseases:
… Is the Oxidation of vital DNA, Proteins, and Lipids,
which leads to Mutations, Loss of Function, Activation of Inflammation and Cell-Death Pathways.
This Molecular Damage initiates a Wide Range of Diseases including: Neurodegenerative Disorders (Alzheimer’s, ALS, Parkinson’s), Cardiovascular Disease (Atherosclerosis, Stroke), Liver Disease (NAFLD), Chronic Inflammatory and Autoimmune Conditions (COPD, Rheumatoid Arthritis, Lupus), Diabetes Complications, and Mitochondrial or Metabolic Disorders.